3. Petroleum Products
Fuel:
- Any substance that gives off heat and energy when burned is called a fuel.
- Wood, charcoal, petrol, diesel and natural gas are some of the fuels we use in our daily life
Types of fuels:
Solid fuels:
- Wood and coal are solid fuels because they are solid.
- First used by man.
- They are easy to store and carry. The production cost of these is also low.
Liquid fuels:
- Derived from fossils of dead plants and animals.
- Some liquid fuels are petroleum oil, charcoal and alcohol.
- Gives more energy when burning. Also, they do not produce ash.
Gaseous fuels:
- Gaseous fuels include coal gas, oil gas, producer gas and hydrogen gas.
- They do not cause pollution.
Properties of ideal fuel:
- Should be readily available.
- Should be easily transportable.
- Should be available at low cost.
- Should have high calorific value.
- To release more heat.
- Do not give unpleasant substances after burning.
Fuel efficiency:
Specific Energy:
- The thermal energy released when a certain mass of fuel burns is called its energy.
- It is defined as energy per mass of oil which is used to measure the energy stored in fuels.
- Its SI unit is Jkg -1
Caloric value:
- It is the amount of heat energy released by the complete combustion of a fuel at constant pressure under normal conditions.
- It is measured in units of K/g
Octane No:
- It is a number indicating the amount of hydrocarbon in petrol called octane.
- A fuel with a high octane number is a good fuel.
Ticket no:
- To measure the ignition delay time of the fuel in a diesel engine.
- Fuel with higher cetane number has shorter ignition time.
- A fuel with a high cetane number is called a good fuel.
Petroleum:
- Petroleum is referred to as “black gold”.
- Crude oil is considered the “mother of all commodities”,
- Crude oil is used to make various products like medicines, plastics, petrol, synthetic fabrics etc.
- Petroleum has been the world’s leading source of energy since the 1950s.
- Petroleum is a liquid found naturally in rock formations. It consists of a complex mixture of different molecular weights of hydrocarbons and other organic compounds.
- Petroleum is also a raw material for many industrial products, including pharmaceuticals, solvents, fertilizers, pesticides, synthetic fragrances, and plastics.
- The word petroleum is derived from the Greek word “Petra” and the Latin word “oleum”. It means “shale oil”.
- After coal, petroleum is the next largest source of energy in India.
- It provides raw materials for various manufacturing industries. Petroleum refineries act as “nodal industries” for synthetic textiles, fertilizers and numerous chemical industries.
- Locations where petroleum is found
- Crude oil was first extracted from the ground in China 2500 years ago
- The world’s first crude oil well was drilled in 1859 in Pennsylvania, USA.
- The second oil well was drilled in 1867 at Makum in Assam, India.
- The world’s leading petroleum producing countries are the United States, Kuwait, Iraq, Iran, Russia and Mexico.
- In India, petroleum is found in Assam, Gujarat, Maharashtra (OLD 600U), Andhra Pradesh (Godavari and Krishna basins), Tamil Nadu (Cavery basin).
- Petroleum is extracted as a dark liquid by drilling deep wells into the earth.
Petroleum formation:
- Petroleum is formed from the remains of dead plants and animals.
- When plants and animals die, they sink and settle at the bottom of the ocean.
- Millions of years ago, these dead wildlife and plants decomposed into sand and silt.
- Some bacteria help in the decomposition of these organic materials and cause some chemical changes.
- Material rich in carbon and hydrogen is left behind. However, because there is not enough oxygen at the bottom of the ocean, the material is unable to decompose completely.
- Partially decomposed material from the seabed, eventually covered by multiple layers of sand and silt.
- This burial took millions of years and finally, due to high temperature and pressure, the organic matter completely decomposed to form oil.
Petroleum-refining:
- Petroleum refineries are very large industrial complexes consisting of numerous processing units and ancillary installations such as utility units and storage tanks.
- There crude oil is extracted and converted into more valuable products such as petroleum naphtha, gasoline, jet fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, petroleum kerosene and liquefied gas.
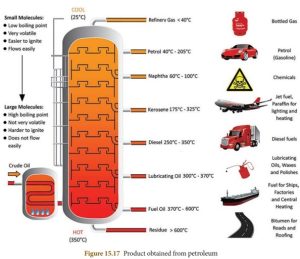
- Petroleum is a mixture of many substances like gas, petrol, diesel, kerosene, lubricating oil, paraffin wax.
- Since these components serve different purposes, it is important to separate them or in other words to refine the crude oil. This process of separating the various components of petroleum is called petroleum refining.
- It is done in oil refineries.
Three-step process:
Extraction of water:
- Salt water is found along with crude oil from oil wells.
- The oil is separated into various components through the distillation process. The heavier elements settle to the bottom while the lighter elements rise as vapor or liquid.
- In the first step this brine is extracted from the crude oil.
Extraction of sulfur compounds:
- Sulfur compounds are contaminants in crude oil.
- These pollutants are excreted.
Back Distillation:
- Petroleum is a compound.
- The fractions are separated by post-distillation. Heating a mixture of liquids of different boiling points, separating them and cooling them is called retro distillation.
- Crude petroleum is first heated in a furnace to a temperature of 400°C.
- As the crude oil vapor reaches the top of the furnace, their various fractions separate based on boiling point.
- In a process called conversion, chemical processing is used on some fractions to form others.
- For example, chemical processing can split long chains into shorter chains. This allows a refinery to convert diesel fuel into gasoline depending on the gasoline demand.
- In industry, the refining process is commonly known as the “downstream” sector, while the “upstream” sector is known as crude oil production.
- The term downstream is synonymous with the idea of a commodity moving from its supply chain to an oil refinery to be refined into gasoline.
- The downstream phase also includes the actual sale of petroleum products to other companies, governments or private individuals.
Applications of petroleum:
Refined products derived from crude oil have many uses.
- Liquefied petroleum gas or LPG is used in homes and industry.
- Used as fuel for diesel and petrol vehicles. Diesel is generally preferred for heavy motor vehicles.
- Petrol is also used as a solvent for dry cleaning, whereas diesel is also used to run electricity generators.
- Kerosene is used as fuel for stoves and jets.
- Lubricant reduces wear and corrosion of engines.
- Paraffin wax is used to make candles, ointments, ink, crayons, etc.
- Bitumen or asphalt is mainly used to surface roads.
