4. Fertilizers and Pesticides.
Fertilizers:
Introduction and Classification a fertilizer is a substance used to supply essential elements like nitrogen, phosphorous, potassium to the soil. The essential qualities of good fertilizer are as follows.
- The nutrient elements present in the fertilizer should be readily available to the plants.
- It should not damage the plants
- It should be fairly soluble in water so as to enable it to dissolve in soil
- It should be stable
- It should be able to adjust the acidity of the soil
- Fertilizers must to be converted into a form which the plant can assimilate easily
- It should be cheap
- It should not produce extra heat that can damage the plant
Classification of Fertilizer:
Nitrogenous Fertilizers:
These type of fertilizers generally supply nitrogen to the soil.
Examples: Ammonium Sulphate [(NH4)2SO4], Calcium ammonium nitrate (CAN, basic calcium ammonium nitrate Ca (NO3)2CaO, Calcium cynamide CaNCN, urea etc.
Phosphorous Fertilizers:
These fertilizers provide phosphorous to the soil.
Examples: Super phosphate of lime, triple super phosphate, phosphate slag, Ammoniated phosphates, Nitro phosphate
Potash Fertilizers:
These fertilizers provide potassium to the plant.
Examples: Potassium chloride, Potassium sulphate, Potassium Nitrated etc.
NP Fertilizers:
These fertilizers contain two elements i.e., sodium and phosphorous. These are formed by mixing together both the fertilizers.
Example: dihydrigen ammoniated phosphate (NH4H2PO4), Calcium superphosphate [Ca(H2PO4)2 2Ca(NO3)2].
NPK or complete fertilizers:
These type of fertilizers provide all the three essential elements viz nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium to the soil. It is obtained by mixing all the three types of fertilizers in suitable preparations.
Nitrogenous Fertilizers:
Ammonium sulphate or sindri fertilizers (NH4)2SO4:
It is prepared by manufactured at sindri fertilizer factory Bihar. Hence it is called sindri fertilizers. This fertilizer contains 24-25% ammonia which is converted to nitrates in the soil by nitrifying bacteria.
Calcium ammonium nitrate (CAN) (Nangal Fertilizer):
[Ca (NO3)2NH4NO3], It is manufactured in the following manner.
Production of Ammonia: Haber’s process
Production of nitric acid: It is obtained by Ostwald’s process. This process ammonia mixed with air in the ratio 1: 10 by volume. In this process nitric Oxide (NO) is produced.
![]()
Formation of NH4NO3:
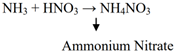
Formation of CAN pellets: The concentrates solution of NH4ON3 is stirred with finally powdered lime stone.
![]()
CAN is very hygroscopic hence to protect it from atmospheric moisture the pellet of CAN are stirred with concentrated solution of finely powdered soap stone (Sodium Silicate). The pellets are then dried and packed in polythene bags. This fertilizers is manufactured in Mangal (Punjab) and Rourkela. CAN contain 20% nitrogen. It can be directly assimilated by plants, it is highly soluble in water.
Basic Calcium nitrate Ca (NO3)2.CaO:
It is manufactured by the following process.
Production of calcium nitrate: When lime stone (CaCO3) is neutralized by nitric acid and the solution obtained is evaporated when the crystals of Ca (NO3)2.4H2O are obtained.
![]()
Production of Ca (NO3)2CaO: When Ca (NO3)2 is mixed with excess of quick lime, basic calcium nitrate is obtained.
![]()
It is hygroscopic and is soluble in water. It is basic in nature and can be directly assimilated by the plants.
Calcium Cynamide (CaCN2):
This compound is a derivative of cynamide (H2CN2). It is manufactured by the action of air on lime stone and coal. The lime stone is burnt in kilns to obtain lime (CaO). A mixture of lime and coal is heated in an electric furnace at 2500◦C to produce calcium carbide (CaC2) It is finely powdered and then heated in a cylindrical electric furnace at 1000◦C in the atmosphere of nitrogen, when CaCN2 is produced.
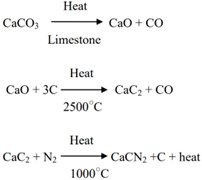
Grey Calcium Cynamide:
It is sparingly soluble in water. This ammonia is converted into nitrates by nitrifying bacteria.
Urea (carbamide NH2CONH2): It is an excellent nitrogenous fertilizer and is manufactured by reacting ammonia and carbon-di-oxide.
![]()
Urea:
Urea separates as dry powder and contains 47% of nitrogen. Urea has the higher nitrogen content than other fertilizers. It cost of production is less and it can be used in all types of crops and soils.
Phosphate Fertilizers:
Super phosphate of lime [Ca (H2PO4)2 + 2 (CaSO4. 2H2O)]:
It is a mixture of calcium dihydrogen phosphate Ca (H2PO4) and dihydrate calcium sulphate (gypsum) CaSO4 2H2O. It contains about 16-20% of P2O5.
![]()
Calcium dihydrogen + gypsumPhosphate Super Phosphate of Lime
Double and Triple Superphosphates:
Triple phosphate is prepared by treating rock phosphate with phosphoric acid in a mixer.
![]()
Phosphatic Slag:
This slag is obtained as a byproduct in the manufacture of steel and is a double salt of tricalcium phosphate and calcium silicate.
Ammoniated phosphate:
It is prepared action of calcium phosphate, sulphuric acid and ammonium sulphate. It contains about 12% of nitrogen and 50.5% of P2O5.
![]()
Potash fertilizers:
Potassium chloride:
It is found in nature as Sylvine (KCl) and carnalite (KCl. MgCl.6H2O). It is extracted from carnalite by boiling with the mother liquor from previous operation. Carnalite dissolves where as other impurities are not dissolved and can be filtered off. It is a white crystalline solid and is fairly soluble in water.
Potassium sulphate (k2SO4): It is manufacture from naturally occurring mineral. Eg. Schonite
![]()
Potassium nitrate or Nitre or Indian Saltpetre (KNO2): Crude Nitre occurs as an efflorescence on the surface of the earth in tropical countries. It is obtained from a mixture of child % petre (NaNO2) and potassium chloride (KCl).
![]()
Pesticides:
Pesticides are legally classed as ‘Economic poisons’ and are defined as any substance used for controlling, preventing, destroying, repelling or mitigating any pest.
Lists the various Pesticides:
S.No | Pesticide class | Functions |
1 | Insecticide | Controls Insects |
2 | Herbicide | Kills weeds |
3 | Fungicide | Kills fungi |
4 | Rodenticide | Kills Rodents |
5 | Bactericide | Kills Bacteria |
6 | Algicide | Kills Algae |
7 | Molluscicide | Kills Snails, Slugs, Mussels, Oyesters |
8 | Avicide | Controls or repels birds |
9 | Slimicide | Controls Slimes |
10 | Piscicide | Controls Fish |
11 | Ovicide | Destroys Eggs |
Classification (on the basis of the method by which insecticides act):
Contact Poison:
Those which kill by direct action on the organism are designated as contact poison. Examples: Chlorinated hydrocarbons, organophosphates, carbonates, pyrethrum, Nicotine sulphate, Rotenone.
Stomach Poison:
Those which act internally after ingestion by the insect are termed as Stomach Poison. Compounds of Arsenic and fluorine are used as stomach poisons. Examples: Lead Arsenate, Calcium Arsenate, Copper Arsenate, cryolite. Sodium fluoride, sodium, barium fluosilicates, Mecury compounds such as HgCl2, boron compounds (boric acid), thalium compound (Tl2SO4), yellow phosphorous and formaldehyde.
Fumigants:
Insecticides which acts in Gaseous state are called fumigants. Examples: HCN gas. Methyl bromide, carbontetrachloride, carbondisulphide, nicotine, naphthalene
Insecticides:
The control of insect pests affecting agricultural crops, domestic animals and man has been of considerable economic importance to mankind since the beginning of civilization.
The Arsenic Compounds Arsenic Oxides:
Arsenic tri oxide As2O3, Arsenic pentoxide or Arsenic acid As2O5.
Calcium Arsenates: Ca3 (AsO4)2] Ca (OH) 2
Lead Arsenates: PbHASO4
Magnesium Arsenates: Mono magnesium ortho Arsenate MgH4 (AsO4)2, secondary magnesium ortho Arsenate MgHAsO4 and Tri magnesium ortho Arsenate Mg2 (AsO4)2
Fluorine Compounds:
Sodium Fluoride (NaF): The first Fluorine compound used against cockroaches. It is also used as Herbicide.
Zinc fluoride (ZnF2): Used as wood Preservative.
Calcium Fluorspar, magnesium, Strontium, Copper, barium and lead fluorides are tested against mosquito larvae.
Sodim and potassium fluosilicate Na2SiF6 and K2SiF6 are used against mosquito larvae.
Sodium aluminium fluosilicate, Sodium fluo aluminates Na3AIF6
Boron Compounds:
Boric acid (H3BO3) has been used as an ingredient of cockroach baits and to kill housefly larvae in manure.
Borax (Na2B4O7.10H2O): It is used as fly preventive in manure and ant poison
Barium and Calcium borates
Mercury compounds:
Metallic mercury has been found to function as a fumigant.
Mercuric chloride HgCl2: It has been used as fungicide and Bacteriacide.
Mercuric oxide HgO
Ethyl mercuric chloride (C2H5 HgCl), Ethyl mercuric Iodide – (C2H5HgI) and Ethyl mercuric phosphate.
Phenyl mercuric salts (C6H5HgX): Acetate, Benzoate, phthalate, Salicylate, Gluconate
Hydroxy mercurichlorophenol, hydroxy mercuricresol.
Copper Compounds:
Bordeaux mixture (CuSO4 + Ca(OH)2
Solution made up of copper sulphate, quick lime and water in fixed ratios. It is used as Fungicide.
Burgundy mixture:
It is known as soda Bordeuax and is prepared by the reaction of copper sulphate, pentohydrate and sodium carbonate solution.
Sulphur Compounds:
Sulphur dioxide (SO2) is used as household fumigant.
Modern Insecticides:
Organo Chlorine Insecticides:
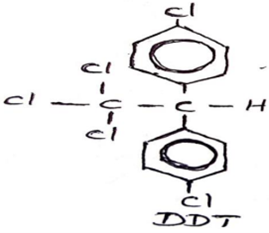
DDT: Dichiloro Diphenyl Trichloro Ethane
DDT is prepared from Chloro Benzene and trichloro acetaldehyde
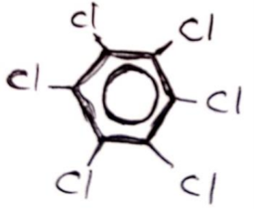
BHC (Benzene Hexa Chloride)
DDD (Dichloro Diphenyl Dichloro Ethane)
Lindane
Endosulfan
Organo Phosphorous Insecticides:
Organo Phosphorous Insecticides are Malathion, Parathion, TEPP, Thimet, Tetram, Phosdrin, and Paraoxon HETP.
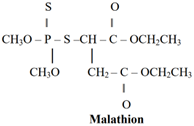
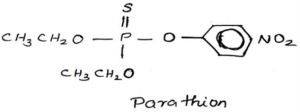
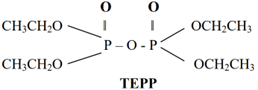
Carbamate Insecticides:
Carbamate Insecticides are Carbary (Sevin), Aldicarb (? Temik), Penuron, Monuron, Sectron.
Some Important Herbicides:
Some important Herbicides are 2, 4 D (2, 4 dichlorophenoxy acetic acid), 2, 4, 5 – T (2, 4, 5 tri – chlorophenoxy acetic acid), atrazine, picioram, propazine.
Some Important Rodenticides:
Some important Rodentiocides are Strychnine, Arsenic, Zinc phosphate, warparin, sodiul fluoro acetate, thalium phosphorous, ANTU (alpha naphthyl urea) and Norbromide.
