10. Heat
Mercury or Alcohol is Used in Thermometer:
- Mostly Alcohol and Mercury are used in thermometers as they remain in liquid form even with a change of temperature in them.
- A small change in the temperature causes change in volume of a liquid.
- We measure this temperature by measuring expansion of a liquid in thermometer.
Properties of Mercury: –
- Its expansion is uniform. (For equal amounts of heat it expands by equal lengths.)
- It is opaque and shining.
- It does not stick to the sides of the glass tube.
- It is a good conductor of heat.
- It has a high boiling point (357°C) and a low freezing point (−39°C). Hence a wide range of temperatures can be measured using a mercury thermometer
Properties of Alcohol:
- The freezing point of alcohol is less than −100°C. So it can be used to measure very low temperatures.
- Its expansion per degree Celsius rise in temperature is very large.
- It can be colored brightly and hence is easily visible.
State the working of temperature controller:
- A thermostat is a device which maintains the temperature of a place or an object constant.
- The word thermostat is derived from two Greek words, ‘thermo’ meaning heat and ‘static’ meaning staying the same.
- Thermostats are used in any device or system that gets heated or cools down to a pre-set temperature.
- It turns an appliance or a circuit on or off when a particular temperature is reached.
- Devices which use thermostat include building heater, central heater in a room, air conditioner, water heater, as well as kitchen equipments including oven and refrigerators. Sometimes, a thermostat functions both as the sensor and the controller of a thermal system.
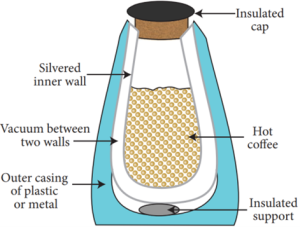
Thermo Flask:
- The thermos flask (Vacuum flask) is an insulating storage vessel that keeps its content hotter or cooler than the surroundings for a longer time.
- It is primarily meant to enhance the storage period of a liquid by maintaining a uniform temperature and avoiding the possibilities of getting a bad taste.
Working of Thermos flask:
- A thermos flask has double walls, which are evacuated.
- It is silvered on the inside.
- The vacuum between the two walls prevents heat being transferred from the inside to the outside by conduction and convection.
- With very little air between the walls, there is almost no transfer of heat from the inner wall to the outer wall or vice versa.
- Conduction can only occur at the points where the two walls meet, at the top of the bottle and through an insulated support at the bottom.
- The silvered walls reflect radiated heat back to the liquid in the bottle.
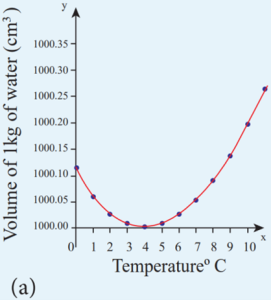
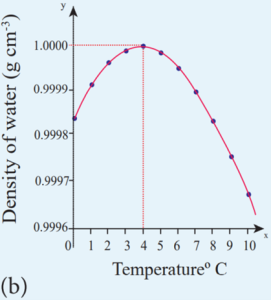
Anomalous Expansion of Water:
- Liquids expand on heating and contract on cooling at moderate temperatures. But water exhibits an anomalous behavior.
- It contracts on heating between 0˚C and 4˚C.
- The volume of the given amount of water decreases as it is cooled from room temperature, until it reach 4˚C.
- Below 4˚C the volume increases and so the density decreases.
- This means that the water has a maximum density at 4˚C.
- This behavior of water is called anomalous expansion of water.
- In cold countries during the winter season, the surface of the lakes will be at lower temperature than the bottom.
- Since the solid water (ice) has lower density than its liquid form, below 4°C, the frozen water will be on the top surface above the liquid water (ice floats).
- This is due to the anomalous expansion of water.
- As the water in lakes and ponds freeze only at the top the species living in the lakes will be safe at the bottom.
Our eye is sensitive to only visible wavelength (in the range 400 nm to 700nm):
- The Sun is approximately taken as a black body.
- Since any object above 0 K will emit radiation, Sun also emits radiation.
- Its surface temperature is about 5700 K.
Wien’s Law and Vision:
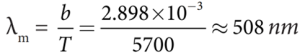
- It is the wavelength at which maximum intensity is 508nm.
- Since the Sun’s temperature is around 5700K, the spectrum of radiations emitted by Sun lie between 400 nm to 700 nm which is the visible part of the spectrum.
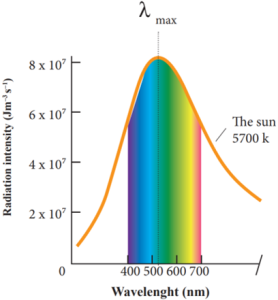
- The humans evolved under the Sun by receiving its radiations.
- The human eye is sensitive only in the visible not in infrared or X-ray ranges in the spectrum.
- Suppose if humans had evolved in a planet near the star Sirius (9940K), then they would have had the ability to see the Ultraviolet rays!
Temperature increase by non-heat transfer phenomenon:
- This is a process in which no heat flows into or out of the system (Q=0).
- But the gas can expand by spending its internal energy or gas can be compressed through some external work.
- So the pressure, volume and temperature of the system may change in an adiabatic process.
- For an adiabatic process, the first law becomes ΔU = −W.
- This implies that the work is done by the gas at the expense of internal energy or work is done on the system which increases its internal energy.
The adiabatic process can be achieved by the following methods:
- Thermally insulating the system from surroundings so that no heat flows into or out of the system; for example, when thermally insulated cylinder of gas is compressed (adiabatic compression) or expanded (adiabatic expansion).
- If the process occurs so quickly that there is no time to exchange heat with surroundings even though there is no thermal insulation.
Examples:
- When the tyre bursts the air expands so quickly that there is no time to exchange heat with the surroundings.
- When the gas is compressed or expanded so fast, the gas cannot exchange heat with surrounding even though there is no thermal insulation.
- When the warm air rises from the surface of the Earth, it adiabatically expands.
- As a result the water vapor cools and condenses into water droplets forming a cloud.
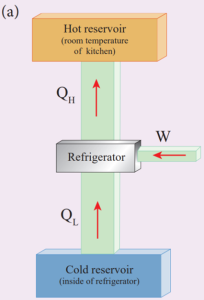
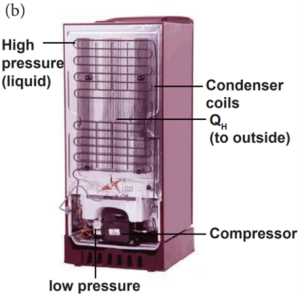
Refrigerator Works:
A refrigerator is a Carnot’s engine working in the reverse order.
Working Principle:
- The working substance (gas) absorbs a quantity of heat QL from the cold body (sink) at a lower temperature TL.
- A certain amount of work W is done on the working substance by the compressor and a quantity of heat QH is rejected to the hot body (source) ie, the atmosphere at TH.
- When you stand beneath of refrigerator, you can feel warmth air.
From the first law of thermodynamics, we have
![]()
As a result the cold reservoir (refrigerator) further cools down and the surroundings (kitchen or atmosphere) gets hotter.
Coefficient of performance (COP) (β):
COP is a measure of the efficiency of a refrigerator. It is defined as the ratio of heat extracted from the cold body (sink) to the external work done by the compressor W.
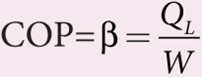
From the equation
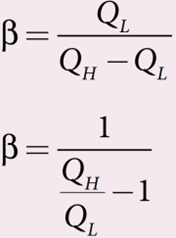
But we know that
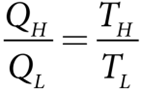
Substituting this equation into equation, we get
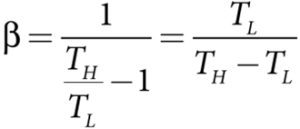
Inferences:
- The greater the COP, the better is the condition of the refrigerator.
- A typical refrigerator has COP around 5 to 6.
- Lesser the difference in the temperatures of the cooling chamber and the atmosphere, higher is the COP of a refrigerator.
- In the refrigerator the heat is taken from cold object to hot object by doing external work.
- Without external work heat cannot flow from cold object to hot object.
- It is not a violation of second law of thermodynamics, because the heat is ejected to surrounding air and total entropy of (refrigerator + surrounding) is always increased.
Refrigerator:
- In hot summer, we use earthen pots to drink cold water.
- The pot reduces the temperature of water inside cyclic process is the basic necessity for heat engine or refrigerator.
- In earthen pot, the cooling process is not due to any cyclic process.
- The cooling occurs due to evaporation of water molecules which oozes out through pores of the pot.
- Once the water molecules evaporate, they never come back to the pot.
- Even though the heat flows from cold water to open atmosphere, it is not a violation of second law of thermodynamics.
- The water inside the pot is an open thermodynamic system, so the entropy of water + surrounding always increases.
